Painstaking Lessons Of Info About How To Test DC Bus

05 DC Accessory Bus Wiring YouTube
Understanding Your DC Bus
1. What Exactly Is a DC Bus, Anyway?
Alright, let's talk about the DC bus. Think of it like the main artery in your electrical system — it's the central hub that distributes direct current (DC) power to all the different components that need it. In simpler terms, it's the highway where electrons travel to power your gadgets, motors, and whatnot. It's found in everything from electric vehicles to solar power setups and industrial equipment.
Unlike AC (alternating current), which constantly changes direction, DC flows in one consistent direction. This makes it ideal for powering electronic devices and storing energy in batteries. So, the DC bus takes the DC power source (like a battery or a rectified AC source) and efficiently delivers it to where it's needed.
Now, why is this important? Well, without a healthy DC bus, your entire system can grind to a halt. Voltage fluctuations, excessive ripple, or plain old component failure can all wreak havoc. That's why testing your DC bus regularly is crucial. It's like checking your car's oil — preventative maintenance keeps everything running smoothly (and prevents costly breakdowns later on).
Essentially, if you value having functional electronics, understanding and maintaining your DC bus is a must. So buckle up, because we're about to dive into how to make sure yours is in tip-top shape!
Why Bother Testing Your DC Bus? (Besides Avoiding Electrical Armageddon)
2. The Many Benefits of Proactive Testing
Okay, so you might be thinking, "Do I really need to test my DC bus?" The short answer is: yes, absolutely! Neglecting your DC bus can lead to a whole host of problems, ranging from minor inconveniences to catastrophic failures (and nobody wants that!). Let's break down why testing is so important.
First and foremost, testing helps you identify potential problems before they become major headaches. Catching a voltage fluctuation or an excessive ripple early on can prevent damage to sensitive electronic components. Think of it as early detection for your electrical system — it's always better to be proactive.
Secondly, regular testing can improve the overall efficiency of your system. A well-maintained DC bus delivers power more effectively, reducing energy waste and potentially lowering your electricity bill. It's like tuning up your engine — a smoother-running system is a more efficient system.
Finally, and perhaps most importantly, testing your DC bus helps ensure the safety of your equipment and personnel. A faulty DC bus can create dangerous conditions, such as overheating or electrical arcing. By identifying and addressing potential hazards early on, you can prevent accidents and keep everyone safe. It's a simple matter of playing it safe.

Tools of the Trade
3. Gearing Up for Electrical Success
Before you jump into testing your DC bus, you'll need to gather the right tools. Having the proper equipment will make the process much easier, safer, and more accurate. Think of it like cooking — you wouldn't try to bake a cake without an oven, would you?
The most essential tool is a digital multimeter (DMM). A good DMM will allow you to measure voltage, current, and resistance with precision. Make sure it's a reliable brand and that you know how to use it safely. Read the manual! Seriously, it's there for a reason.
Next up, you'll need an oscilloscope. This handy device displays voltage signals over time, allowing you to visualize any fluctuations or ripple in your DC bus voltage. An oscilloscope is invaluable for detecting subtle problems that a DMM might miss. It's like having a magnifying glass for your electrical signals.
Finally, don't forget about safety gear! Wear safety glasses and insulated gloves to protect yourself from electrical shock. Also, make sure to disconnect the DC bus from its power source before testing, unless otherwise instructed. Safety first, always! It's better to be cautious than end up with a shocking experience (pun intended!).

A Guide To The Washington, DC Bus Routes, Schedules, And Fares
Step-by-Step
4. Putting Theory into Practice
Alright, you've got your tools, you've got your safety gear, now it's time to get down to business. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to test your DC bus:
Step 1: Visual Inspection. Before you even touch anything with a meter, give the DC bus a good visual inspection. Look for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, burnt components, or loose connections. If you spot anything suspicious, address it before proceeding.
Step 2: Voltage Measurement. Use your DMM to measure the DC voltage at various points along the bus. Compare your readings to the expected voltage levels. Significant deviations could indicate a problem. Remember to select the correct voltage range on your DMM.
Step 3: Ripple Measurement. Use your oscilloscope to measure the ripple voltage on the DC bus. Excessive ripple can damage sensitive components. Check the manufacturer's specifications for the maximum allowable ripple voltage. Turn on AC coupling on your oscilloscope channel to see the ripple more clearly.
Step 4: Load Testing (Optional). If possible, apply a load to the DC bus and repeat the voltage and ripple measurements. This will help you assess how the bus performs under real-world conditions. Make sure the load you apply is within the DC bus's rated capacity!
Step 5: Record Your Findings. Keep a log of your measurements and any observations you make. This will help you track the performance of your DC bus over time and identify any trends. Its also helpful if you need to troubleshoot later. Think of it as a logbook for your bus.
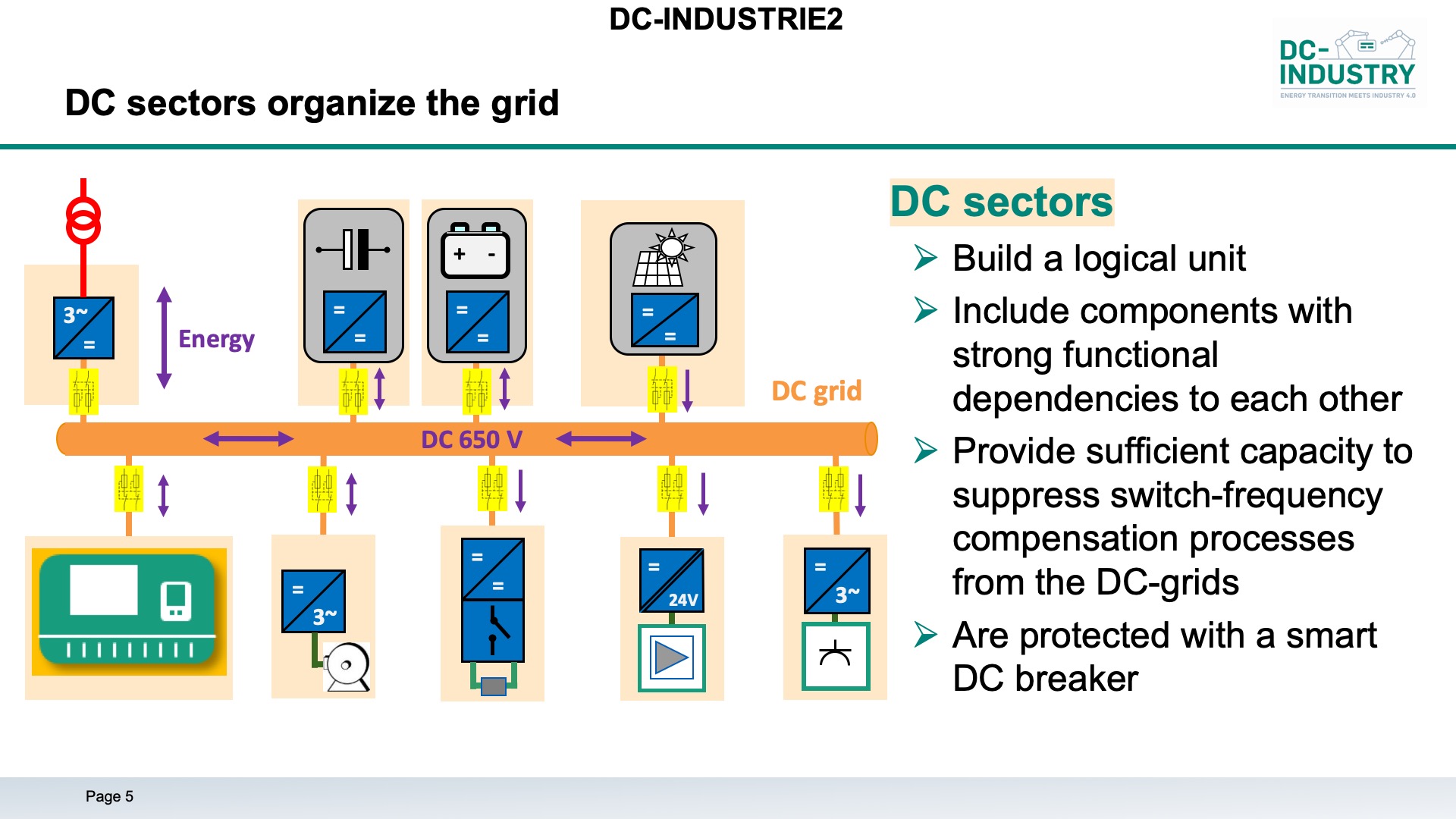
DC Industrie
Interpreting Your Results
5. Decoding the Electrical Signals
So, you've taken your measurements, and now you're staring at a bunch of numbers and waveforms. What do they actually mean? Let's break down how to interpret your results.
Voltage Issues: If your voltage readings are significantly higher or lower than expected, it could indicate a problem with the power source, wiring, or components connected to the DC bus. A low voltage could be due to a failing power supply or excessive load, while a high voltage could be due to a regulator malfunction.
Excessive Ripple: Ripple voltage is the small AC component that rides on top of the DC voltage. Excessive ripple can damage sensitive electronic components and cause them to malfunction. Common causes of excessive ripple include failing capacitors, rectifier diodes, or poor grounding.
Fluctuations: Sudden voltage fluctuations can indicate intermittent connections, loose wires, or failing components. Use your oscilloscope to capture these transient events. A fluctuating voltage is like a flickering light — something's not quite right.If you're unsure about your results, don't hesitate to consult with a qualified electrician or electronics technician. They can help you diagnose the problem and recommend the appropriate solutions.

DC Power Distribution Network With 2 Buses, And One DCT. In This
Troubleshooting Common Problems
6. Fixing What Ails Ya
Okay, so you've identified a problem with your DC bus. Now what? Here are some common issues and how to troubleshoot them:
Low Voltage: Start by checking the power source. Is it providing the correct voltage? If so, check the wiring and connections for any signs of corrosion or damage. Also, make sure that the load connected to the DC bus isn't exceeding its capacity. A voltage drop could be due to resistance in the wiring, which could be due to corrosion. Clean those connections!
Excessive Ripple: The most common cause of excessive ripple is failing capacitors. Inspect the capacitors connected to the DC bus for any signs of bulging, leaking, or discoloration. Replace any damaged capacitors with new ones of the same value and voltage rating. Make sure to observe the polarity of the capacitor.
Fluctuating Voltage: Look for loose wires or intermittent connections. Gently wiggle the wires and connectors while monitoring the voltage on your DMM or oscilloscope. If you see any changes, tighten or replace the affected connection. Sometimes, a simple reseating of a connector can work wonders.
Safety First!: Remember, always disconnect the power source before working on any electrical components. If you're not comfortable working with electricity, consult a qualified electrician or electronics technician.