Awe-Inspiring Examples Of Tips About Does Transformer Convert DC To AC
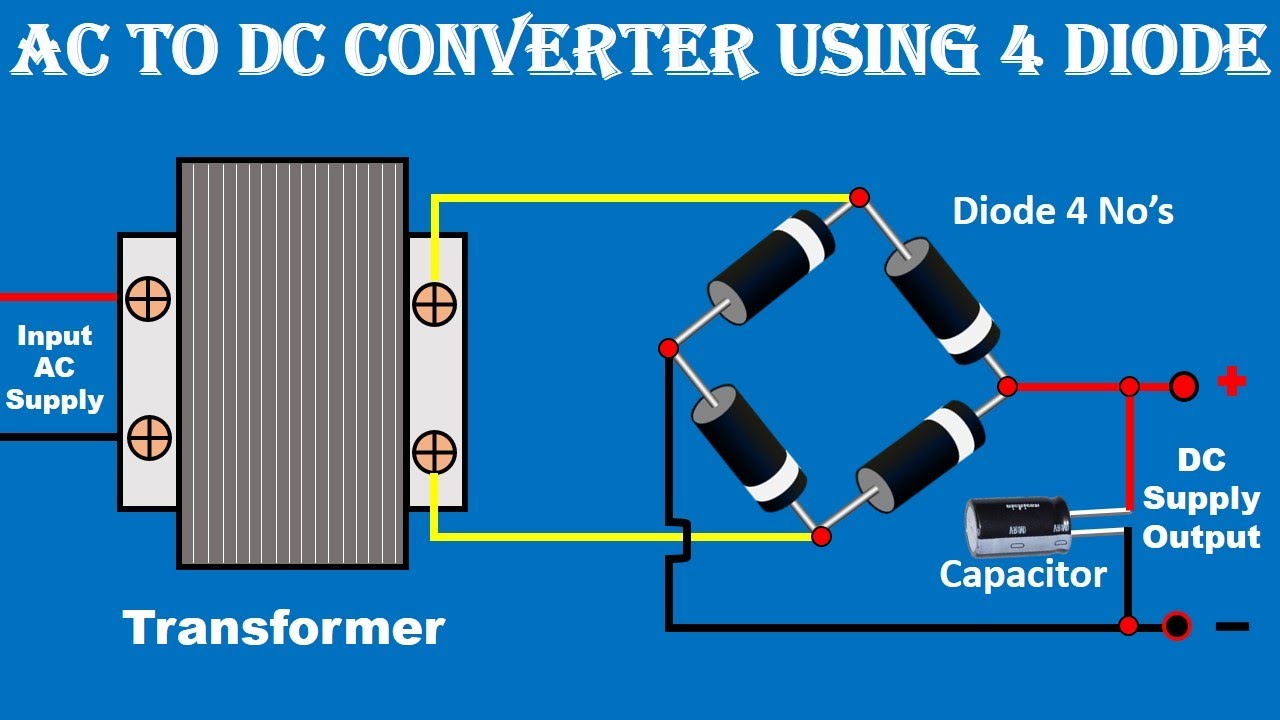
Change Ac To Dc Power Supply
Transformers
1. Unveiling the Transformer's True Calling
Okay, let's tackle a common misconception right off the bat. You might be thinking of transformers as magical boxes that can conjure AC from DC, or vice-versa. Unfortunately, that's not quite their superpower. Think of them more as voltage whisperers. They're really good at taking AC voltage and either boosting it higher or stepping it down lower. Imagine a tiny transformer inside your phone charger transforming the high voltage AC from the wall into a much lower voltage that your phone can safely use. Pretty neat, huh? So, instead of being DC-to-AC converters, they're more like AC voltage modifiers.
The core principle behind a transformer's operation involves the electromagnetic induction between two (or more) coils of wire, electrically isolated but magnetically linked. When alternating current flows through the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field. This changing magnetic field, in turn, induces a voltage in the secondary coil. Because it needs a changing magnetic field, a constant DC voltage won't do the trick. It's like trying to start a campfire with a single match — you need constant friction, not just a static spark.
Now, why is this important? Well, understanding that transformers work solely with AC helps you troubleshoot electrical systems correctly. Imagine trying to fix a faulty device that relies on stepped-down AC voltage, but you're mistakenly checking for a DC component at the transformer's output. You'd be chasing a ghost! Knowing the fundamental principles allows for more efficient and accurate diagnostics.
To summarise it all, transformers are wizards with AC voltages. They can either step them up or step them down, making them indispensable in a whole range of applications, from powering our homes to running complex industrial equipment. But they don't convert DC to AC, so don't expect them to! They're strictly AC-only players. They're crucial components in AC power distribution, ensuring that electricity gets to us at a safe and usable voltage. So the next time you see a transformer, appreciate its specialized role in managing alternating current.

So, What Does Convert DC to AC Then? Enter the Inverter!
2. The Real DC-to-AC Hero
If a transformer isn't the device for converting DC to AC, then what is? The answer is an inverter. Inverters are electronic circuits specifically designed to take a DC input and produce an AC output. Think of solar panels: they generate DC electricity, but most household appliances run on AC. An inverter bridges that gap, transforming the sun's DC bounty into usable AC power for your lights, TV, and other gadgets. They're like the unsung heroes of renewable energy systems!
Inverters are actually quite clever devices. They use electronic switches (like transistors) to rapidly switch the DC voltage on and off in a pattern that mimics an alternating current waveform. The complexity of the circuitry dictates how closely the output resembles a smooth sine wave. Some inverters produce a "modified sine wave," which is a more jagged approximation, while others create a "pure sine wave," nearly indistinguishable from the AC power you get from the grid. Guess which one is kinder to your delicate electronics?
Imagine you're camping, far away from any power outlets. You've got a car battery (DC power) and you want to power a small fan (AC power). You'd use an inverter to convert the battery's DC voltage into the AC voltage required by the fan. Inverters come in all shapes and sizes, from tiny ones for charging your phone in the car to massive industrial-grade units that power entire buildings from battery banks. It all depends on the amount of power you need to convert. This is a simple way to understand how vital the inverter plays.
It's important not to confuse inverters with rectifiers, which do the opposite — convert AC to DC. Rectifiers are commonly found in power supplies, charging adapters, and anything that needs to convert wall power (AC) into the DC voltage required by electronic devices. So, inverters and rectifiers are like two sides of the same coin, each playing a crucial role in manipulating electrical current to suit our needs. These tools all help us get the right kind of electricity to power all our devices.
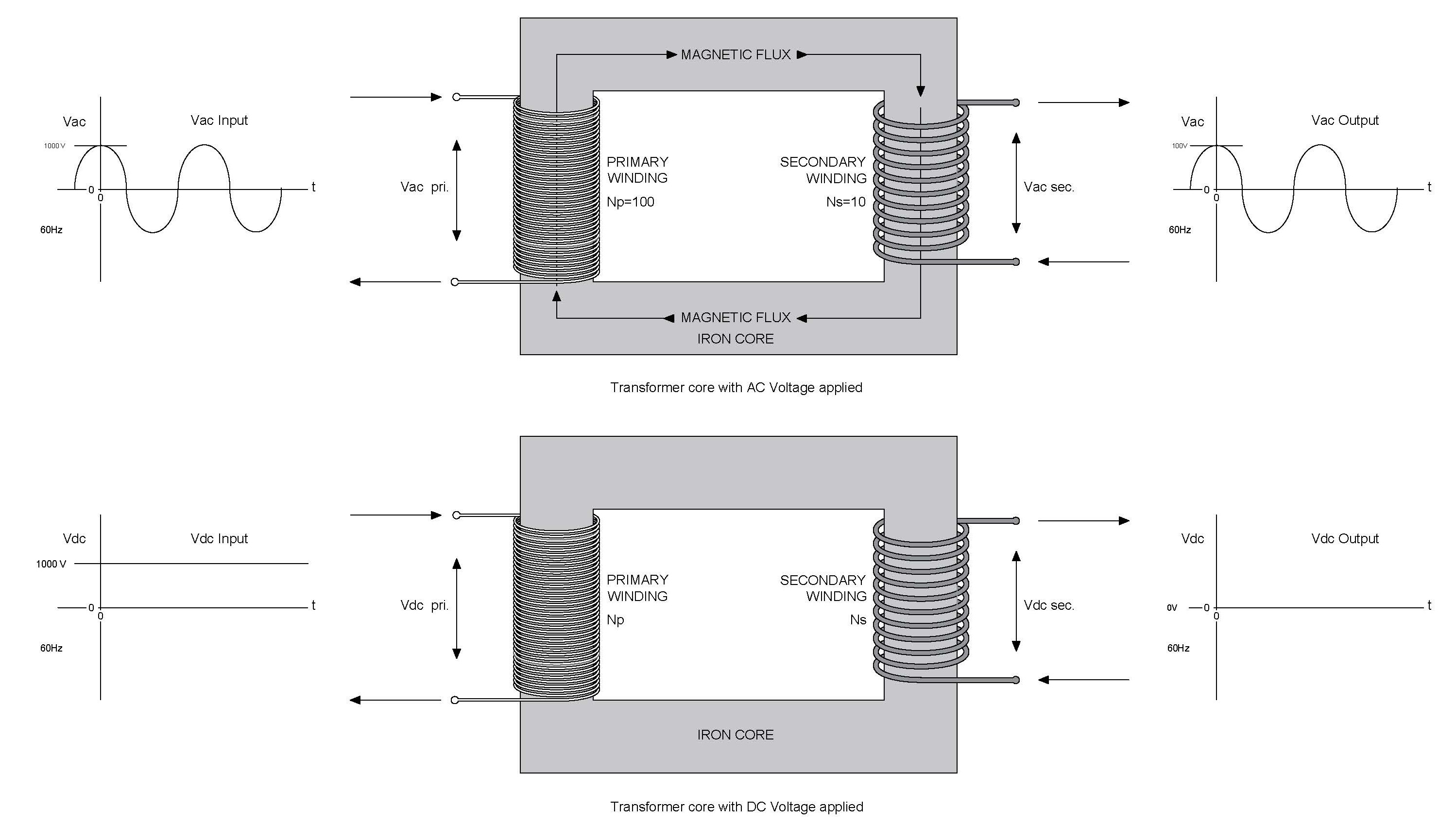
Why This Matters
3. From Power Grids to Portable Gadgets
Understanding the difference between transformers and inverters is more than just trivia; it's essential for comprehending how electrical systems work in the real world. Think about the massive power grid that delivers electricity to our homes and businesses. Power is generated at power plants (often as AC), then stepped up to very high voltages by transformers for efficient long-distance transmission. This reduces energy loss along the wires. At the other end, near our homes, other transformers step the voltage back down to a safer level for consumption.
Consider a portable electronic device like a laptop. The power adapter, sometimes called a "brick," contains both a rectifier to convert AC from the wall outlet to DC and often some regulation circuitry to ensure a stable DC voltage is supplied to the laptop. The laptop itself might contain smaller DC-DC converters to generate the various voltage levels needed by different components. It's a whole symphony of voltage conversion happening right there on your desk!
The development of highly efficient inverters has been a game-changer for renewable energy. Solar power systems rely heavily on inverters to transform the DC electricity generated by solar panels into grid-compatible AC power. Similarly, wind turbines generate AC electricity, but the frequency and voltage can fluctuate depending on wind speed. Inverters are used to synchronize the output with the grid, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply. They're essential for ensuring the power supply is consistent and usable.
In electric vehicles, inverters play a critical role in controlling the motor. The battery pack stores energy as DC, but the electric motor typically requires AC to operate. The inverter converts the DC voltage from the battery into AC voltage with the correct frequency and amplitude to control the motor's speed and torque. It's a complex dance of power electronics that enables the smooth and efficient operation of electric vehicles. Without them, the vehicles would be inoperable!

Ac To Dc Converter Circuit Diagram Pdf
Common Misconceptions and How to Avoid Them
4. Clearing Up the Confusion
One of the most common points of confusion is the difference between voltage conversion and DC-to-AC conversion. Remember, transformers are masters of voltage conversion within AC circuits, while inverters handle the task of changing DC to AC. Thinking of them as interchangeable can lead to incorrect troubleshooting and design decisions. Visualise each tool having a specific role, and stick to that.
Another misconception is that any device plugged into a wall outlet automatically uses AC power. While the wall outlet supplies AC, many electronic devices actually operate internally on DC. These devices use power adapters or power supplies containing rectifiers to convert the AC voltage from the wall into the DC voltage required by their internal components. Therefore, just because something is plugged into AC, doesn't mean it's using AC power itself.
Many people believe that all inverters produce the same quality of AC output. This isn't true! As mentioned earlier, some inverters generate a "modified sine wave," which can be problematic for sensitive electronics. These modified sine wave inverters are often cheaper, but they may cause buzzing sounds in audio equipment or reduce the lifespan of some appliances. Investing in a "pure sine wave" inverter is generally a better choice if you want to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
Finally, a common error is assuming that a transformer can be used to "charge" a battery. Transformers don't store energy; they simply change the voltage of AC power. To charge a battery, you need a dedicated battery charger that provides a regulated DC voltage and current. Attempting to charge a battery directly from a transformer is a recipe for disaster and could potentially damage the battery or create a fire hazard. Think of transformers for voltage conversion, and battery chargers for battery charging!

FAQ
5. Your Burning Questions, Resolved!
Here are some frequently asked questions about transformers and inverters to further clarify their roles and capabilities:
6. What are the main differences between a transformer and an inverter?
A transformer changes the voltage of AC power, while an inverter converts DC power to AC power. Transformers rely on electromagnetic induction, while inverters use electronic switching. They are both very different with individual jobs to perform.
7. Can I use a transformer to power a DC device?
Not directly. You would need a rectifier to convert the AC output of the transformer to DC. The transformer would step down the AC voltage to a suitable level, and the rectifier would then convert it to DC for the device to use. Without the rectifier, it is not possible.
8. Are there any devices that combine the functions of a transformer and an inverter?
Yes, but they are specialized. Some power supplies incorporate both a transformer (for voltage isolation and stepping) and an inverter (for converting DC to AC for specific circuits). However, these are not typically found as stand-alone units doing both tasks simultaneously in a simple way. Often, these are integrated solutions within a more complex piece of equipment.
