Favorite Info About Why Twisted Pair Wire
Twisted Pair Cables How It Works, Application & Advantages
Unraveling the Mystery
1. The Unassuming Hero of Connectivity
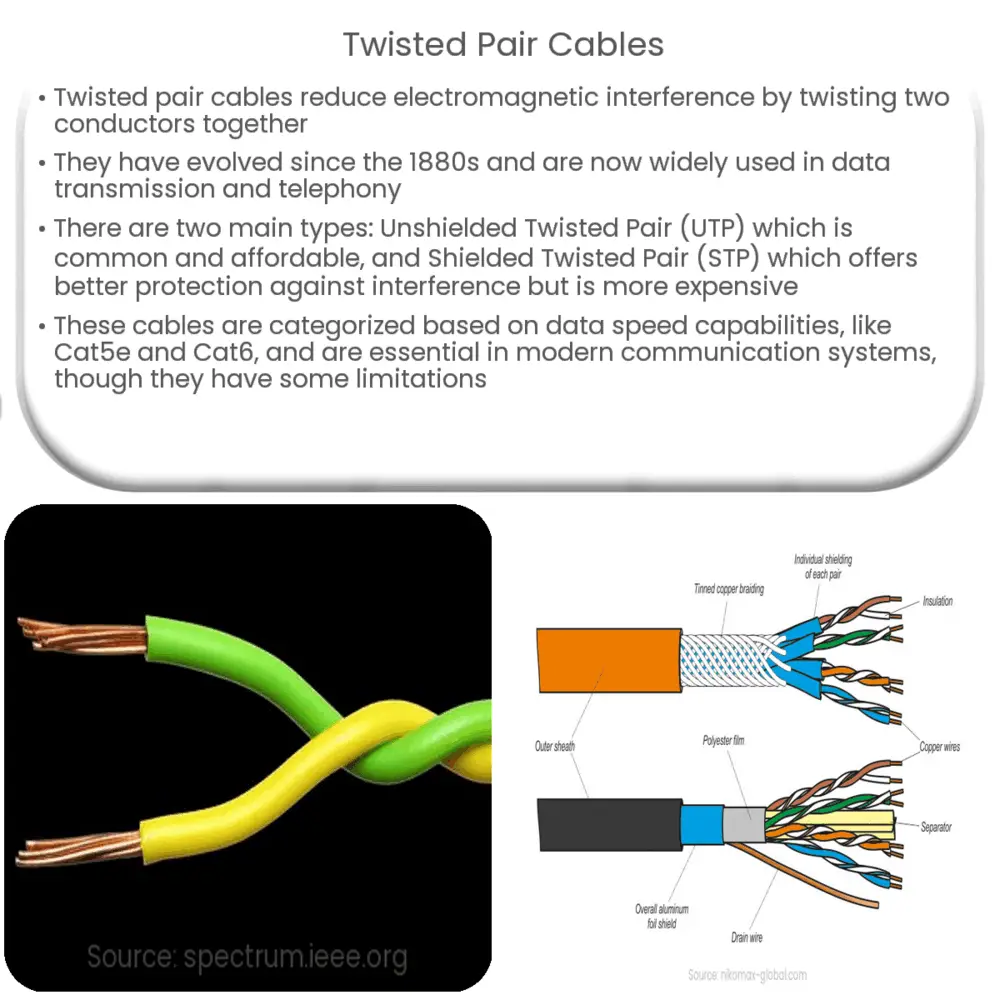
Ever wondered how your internet manages to bring you cat videos and important emails all at the same time? A lot of the credit goes to a humble, often overlooked hero: the twisted pair wire. You've probably seen them those colorful cables snaking behind your computer or router. But what's the big deal with them being twisted? Its not just for looks, I assure you!
Think of it like this: imagine two kids trying to whisper secrets across a noisy playground. If they just shouted, everyone would hear everything! But if they cup their hands around their mouths, focusing the sound, it's much easier to understand each other. That's essentially what twisting does for electrical signals. It helps to focus the signal and reduce interference.
So, why not just use a single, thicker wire? Well, that's where things get interesting. A single wire acts like a little antenna, picking up all sorts of electromagnetic noise floating around — things like radio waves, the hum from your refrigerator, even the static electricity from your socks shuffling across the carpet. All this noise can corrupt the signal, making it harder for your devices to understand the data being transmitted.
By twisting the wires together, engineers cleverly exploit something called "common-mode rejection." In a nutshell, when interference affects the wires, it affects both wires roughly equally. Because the wires are twisted, the receiver can compare the signals and cancel out the common noise, leaving the clean, original signal intact. It's like a built-in noise-canceling headphone system for your data!

The Dance of Twists
2. Finding the Perfect Twist for the Job
Not all twisted pair wires are created equal. You'll find various categories like Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a, each designed for different speeds and distances. The number of twists per inch is a key factor here. More twists generally mean better noise reduction and higher bandwidth, but also higher manufacturing costs.
Cat5e, for instance, is a workhorse for many home and small office networks. It's relatively inexpensive and can handle speeds up to 1 Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps). Cat6, on the other hand, features tighter twists and thicker conductors, allowing it to handle 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10 Gbps) over shorter distances. Cat6a takes it even further, offering improved performance and longer reach for 10 Gbps connections.
Choosing the right category depends on your specific needs. If you're just browsing the web and streaming videos, Cat5e might be perfectly adequate. But if you're running a data-intensive application or want to future-proof your network, Cat6 or Cat6a might be a better choice. Think of it as choosing the right car: a compact car is fine for running errands, but you'll need a truck if you're hauling heavy loads.
And it's not just about speed. Shielding also plays a role. Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) is the most common and cost-effective type, suitable for most environments. Shielded twisted pair (STP) adds a layer of foil or braid around the wires to further reduce interference, making it ideal for noisy industrial settings or environments with sensitive equipment.

Beyond the Office
3. The Versatile Cable That Connects the World
While we often associate twisted pair wires with computer networks, their applications extend far beyond the office. They're used in telephone systems, security cameras, and even some industrial control systems. Their ability to transmit data reliably over relatively long distances makes them a versatile choice for a wide range of applications.
Think about your home phone line (if you still have one!). It probably uses twisted pair wire to connect your phone to the telephone exchange. While digital technologies are becoming more prevalent, twisted pair remains a reliable and cost-effective solution for voice communication.
Even in modern smart homes, twisted pair wires can play a role. They can be used to connect security cameras, smart thermostats, and other devices, providing a stable and secure connection. While Wi-Fi is convenient, wired connections are often more reliable and less susceptible to interference.
So, the next time you see a twisted pair wire, take a moment to appreciate its unsung contributions to our connected world. It's a simple yet ingenious piece of technology that has enabled countless innovations.

Twisted Wire Connectors
Troubleshooting Tips
4. Keeping Your Connections Healthy
Even the best-designed twisted pair cable can run into trouble. Common issues include damaged connectors, loose connections, and excessive cable length. These problems can lead to slow speeds, intermittent connectivity, or even complete network outages.
One of the most frequent culprits is a poorly crimped connector. Ensure that the wires are properly inserted into the connector and that the crimping tool is correctly used. A loose connection can also cause problems. Make sure that the connectors are securely plugged into the devices.
Cable length is another important consideration. Exceeding the maximum recommended length for a particular category of cable can significantly degrade performance. If you need to run a cable over a long distance, consider using a signal repeater or switch to fiber optic cable.
Finally, protect your cables from physical damage. Avoid bending them sharply or exposing them to extreme temperatures or moisture. A little care can go a long way in ensuring the longevity and reliability of your network connections.
The Future of Twisted Pair
5. Adapting to the Ever-Changing Landscape
With the rise of Wi-Fi and other wireless technologies, some might wonder if twisted pair wire is becoming obsolete. The answer is a resounding no! While wireless offers convenience and flexibility, wired connections still provide superior speed, reliability, and security.
In fact, twisted pair wire is often used as the backbone of wireless networks. Wireless access points (APs) typically connect to the network using wired Ethernet cables. This allows the APs to provide high-speed wireless connectivity to devices while maintaining a stable and reliable connection to the network core.
Furthermore, new technologies like Power over Ethernet (PoE) are expanding the applications of twisted pair wire. PoE allows you to power devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points directly through the Ethernet cable, eliminating the need for separate power adapters. This simplifies installation and reduces cable clutter.
So, while wireless is undoubtedly an important part of the future of networking, twisted pair wire will continue to play a vital role for years to come. Its reliability, speed, and versatility make it an indispensable component of modern communication infrastructure.
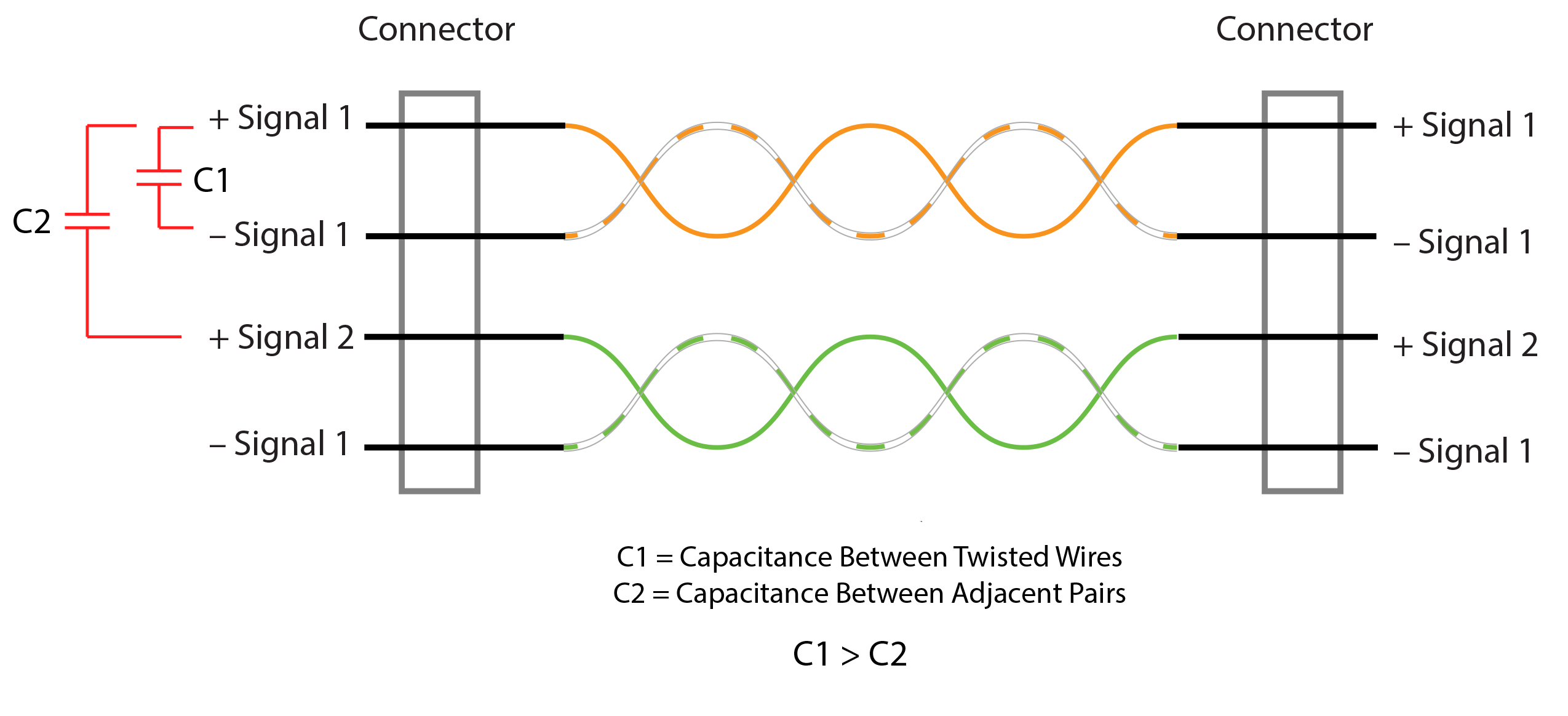
Verifying Twist Pair Relationships Cable & Harness Manufacturing
FAQ
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Q: What's the difference between Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a cables?
A: Think of them like different grades of gasoline. Cat5e is the standard, good for most everyday use. Cat6 is a step up, offering more speed and less interference. Cat6a is the premium option, designed for the highest performance and longer distances.
Q: Can I use any twisted pair cable for any application?
A: Not really. Using the wrong cable can lead to slow speeds or even connection problems. Match the cable category to the requirements of your devices and network. For example, don't use an old Cat5 cable for a 10 Gigabit Ethernet connection.
Q: Is it okay to untwist the wires when terminating a twisted pair cable?
A: Nope, that's a big no-no! Keep the twists as close to the connector as possible. Untwisting the wires increases the risk of interference and reduces performance. Think of it like removing the mufflers from your car — it might sound cool for a second, but you'll quickly regret it.